What is Organic Research in Digital Marketing? A Complete Guide
orgnic research In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, the phrase “organic research” is often thrown around — but what does it actually mean? If you’re a digital marketer, SEO specialist, content creator, or business owner, understanding organic research can help you make smarter, more cost-effective marketing decisions.
In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into what organic research means in digital marketing, why it’s important, how it works, and how you can leverage it to grow your online visibility without spending a dime on ads.
Table of Contents
-
Introduction to Organic Digital Marketing
-
What is Organic Research?
-
Why is Organic Research Important?
-
Key Elements of Organic Research
-
How to Conduct Organic Research: Step-by-Step
-
Tools for Organic Research
-
Real-World Applications of Organic Research
-
Organic vs. Paid Research: What’s the Difference?
-
Final Thoughts
1. Introduction to Organic Digital Marketing
Digital marketing can be broadly divided into organic and paid strategies. Organic digital marketing focuses on methods that don’t require direct payments to platforms, such as:
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
-
Content marketing
-
Social media engagement
-
Email newsletters
Unlike paid advertising (PPC), which gives you immediate visibility but requires ongoing investment, organic strategies grow your brand presence sustainably over time.
2. What is Organic Research?
Organic research is the process of analyzing non-paid search engine results to understand how your website and your competitors are performing organically. It involves gathering insights into:
-
Which keywords bring traffic to your site
-
What content ranks well
-
How your competitors are ranking
-
The backlink profile of top-ranking pages
-
Search trends and user behavior
The goal of organic research is to optimize your digital presence based on actual user intent and behavior, so you can improve your rankings on search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo — without paying for ads.
3. Why is Organic Research Important?
Organic research is a cornerstone of effective SEO and content marketing. Here’s why it’s crucial:
a) Drives Targeted Traffic
By understanding what keywords your audience uses, you can tailor content that directly addresses their needs.
b) Improves ROI
Organic traffic is free, aside from the time and effort you invest. Over time, it delivers a better return on investment than paid ads.
c) Builds Long-Term Value
A well-ranked piece of content can generate traffic for months or even years. Organic research ensures your content stays relevant and competitive.
d) Helps Understand Competitors
Analyzing competitor performance helps identify gaps in your strategy and uncover new opportunities.
4. Key Elements of Organic Research
Let’s break down the core components involved in organic research:
1. Keyword Research
Find out what your audience is searching for. Look for high-volume, low-competition keywords that match their intent.
2. Competitor Analysis
Identify who ranks in the top 10 for your target keywords. Analyze their backlinks, content structure, and keyword strategy.
3. Content Performance
Check which pages on your website generate the most traffic. Are they blog posts? Product pages? This data guides your content creation.
4. SERP Analysis
Study Search Engine Results Pages to understand featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and other SERP features that influence organic visibility.
5. Backlink Profile
Quality backlinks improve your site’s authority. Research which domains link to your competitors and aim to get similar links.
5. How to Conduct Organic Research: Step-by-Step
Here’s a simplified workflow you can follow to start your organic research:
Step 1: Define Your Goals
Are you trying to increase blog traffic? Rank for product keywords? Expand into a new market? Define this before starting.
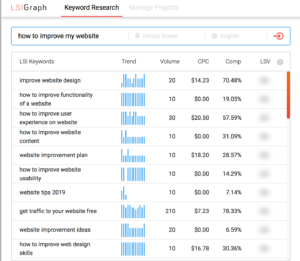
Step 2: Keyword Research
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest to find keywords related to your niche. Focus on:
-
Search volume
-
Keyword difficulty
-
Intent (informational, navigational, transactional)
Step 3: Analyze Competitors
Find out who’s ranking for your target keywords. Use tools like Ahrefs or SpyFu to analyze their backlinks, traffic, and top-performing content.
Step 4: Audit Your Own Site
Look at your current rankings and identify gaps. Use Google Search Console and tools like Screaming Frog to evaluate on-page SEO, broken links, or missing metadata.
Step 5: Monitor Performance
Once you implement changes based on research, monitor the impact. Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track organic traffic and keyword rankings.
6. Tools for Organic Research
Here are some top tools used by professionals for conducting it :
| Tool | Key Features |
|---|---|
| SEMrush | Competitor analysis, keyword research, traffic data |
| Ahrefs | Backlink analysis, keyword explorer, content gap analysis |
| Google Search Console | Tracks keyword rankings, CTR, indexing issues |
| Moz | Keyword difficulty, SERP analysis, link tracking |
| Ubersuggest | Keyword ideas, traffic estimations, domain analysis |
| Screaming Frog | On-page SEO auditing and technical SEO checks |
Each tool offers unique strengths, so you might use a combination depending on your goals and budget.
7. Real-World Applications of Organic Research
Let’s look at a few practical scenarios where it plays a vital role:
a) Blog Strategy
You want to grow your blog traffic. it helps you identify topics your audience cares about and shows you how competitors rank for them.
b) E-Commerce SEO
If you run an online store, it helps you understand what product-related keywords people are searching for — from product reviews to comparison searches.
c) Local SEO
Businesses targeting local customers use it to find location-based keywords and track map rankings.
d) Re-Optimizing Existing Content
Sometimes a blog post is ranking at position 11 (just off Page 1). it can show what’s missing — maybe a backlink, a better title, or more detailed content.
8. Organic vs. Paid Research: What’s the Difference?
| Aspect | Organic Research | Paid Research |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Non-paid search results | Paid ads (Google Ads, Bing Ads) |
| Cost | Time and tools | Ad spend + management fees |
| Time to See Results | Slow (3–6 months) | Immediate |
| Sustainability | Long-term | Stops when budget stops |
| Tools | SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush | Google Ads, SpyFu, Keyword Planner |
Both types of research have value. it is ideal for long-term brand growth, while paid research helps you test quickly or reach new markets instantly.
9. Final Thoughts
Organic research is more than just a behind-the-scenes SEO task — it’s a strategic pillar of modern digital marketing. It empowers you to understand your audience, craft better content, and gain visibility without constantly relying on ad budgets.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned marketer, mastering it will help you:
-
Uncover new keyword opportunities
-
Stay ahead of competitors
-
Improve website visibility
-
Build long-lasting organic traffic
In a digital world where algorithms change and ads get more expensive, it gives you a reliable foundation for sustainable online growth. If you haven’t started yet, now is the perfect time.
you can contact us on whatsapp
